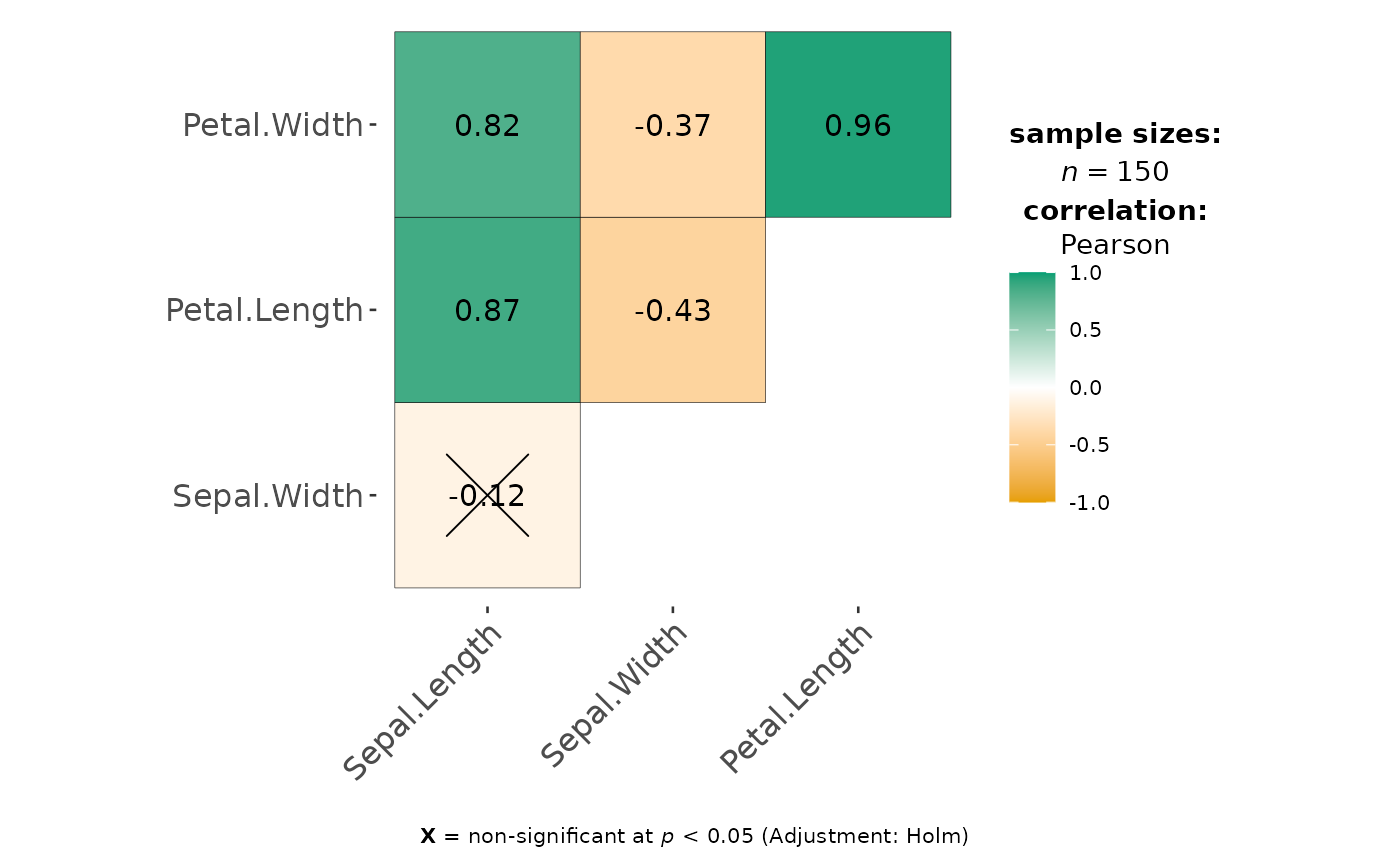
Correlation matrix containing results from pairwise correlation tests.
If you want a data frame of (grouped) correlation matrix, use
correlation::correlation() instead. It can also do grouped analysis when
used with output from dplyr::group_by().
Usage
ggcorrmat(
data,
cor.vars = NULL,
cor.vars.names = NULL,
matrix.type = "upper",
type = "parametric",
tr = 0.2,
partial = FALSE,
digits = 2L,
sig.level = 0.05,
conf.level = 0.95,
bf.prior = 0.707,
p.adjust.method = "holm",
pch = "cross",
ggcorrplot.args = list(method = "square", outline.color = "black", pch.cex = 14),
package = "RColorBrewer",
palette = "Dark2",
colors = c("#E69F00", "white", "#009E73"),
ggtheme = ggstatsplot::theme_ggstatsplot(),
ggplot.component = NULL,
title = NULL,
subtitle = NULL,
caption = NULL,
...
)Arguments
- data
A data frame from which variables specified are to be taken.
- cor.vars
List of variables for which the correlation matrix is to be computed and visualized. If
NULL(default), all numeric variables fromdatawill be used.- cor.vars.names
Optional list of names to be used for
cor.vars. The names should be entered in the same order.- matrix.type
Character,
"upper"(default),"lower", or"full", display full matrix, lower triangular or upper triangular matrix.- type
A character specifying the type of statistical approach:
"parametric""nonparametric""robust""bayes"
You can specify just the initial letter.
- tr
Trim level for the mean when carrying out
robusttests. In case of an error, try reducing the value oftr, which is by default set to0.2. Lowering the value might help.- partial
Can be
TRUEfor partial correlations. For Bayesian partial correlations, "full" instead of pseudo-Bayesian partial correlations (i.e., Bayesian correlation based on frequentist partialization) are returned.- digits
Number of digits for rounding or significant figures. May also be
"signif"to return significant figures or"scientific"to return scientific notation. Control the number of digits by adding the value as suffix, e.g.digits = "scientific4"to have scientific notation with 4 decimal places, ordigits = "signif5"for 5 significant figures (see alsosignif()).- sig.level
Significance level (Default:
0.05). If the p-value in p-value matrix is bigger thansig.level, then the corresponding correlation coefficient is regarded as insignificant and flagged as such in the plot.- conf.level
Scalar between
0and1(default:95%confidence/credible intervals,0.95). IfNULL, no confidence intervals will be computed.- bf.prior
A number between
0.5and2(default0.707), the prior width to use in calculating Bayes factors and posterior estimates. In addition to numeric arguments, several named values are also recognized:"medium","wide", and"ultrawide", corresponding to r scale values of1/2,sqrt(2)/2, and1, respectively. In case of an ANOVA, this value corresponds to scale for fixed effects.- p.adjust.method
Adjustment method for p-values for multiple comparisons. Possible methods are:
"holm"(default),"hochberg","hommel","bonferroni","BH","BY","fdr","none".- pch
Decides the point shape to be used for insignificant correlation coefficients (only valid when
insig = "pch"). Default:pch = "cross".- ggcorrplot.args
A list of additional (mostly aesthetic) arguments that will be passed to
ggcorrplot::ggcorrplot()function. The list should avoid any of the following arguments since they are already internally being used:corr,method,p.mat,sig.level,ggtheme,colors,lab,pch,legend.title,digits.- package, palette
Name of the package from which the given palette is to be extracted. The available palettes and packages can be checked by running
View(paletteer::palettes_d_names).- colors
A vector of 3 colors for low, mid, and high correlation values. If set to
NULL, manual specification of colors will be turned off and 3 colors from the specifiedpalettefrompackagewill be selected.- ggtheme
A
{ggplot2}theme. Default value istheme_ggstatsplot(). Any of the{ggplot2}themes (e.g.,ggplot2::theme_bw()), or themes from extension packages are allowed (e.g.,ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight(),hrbrthemes::theme_ipsum_ps(), etc.). But note that sometimes these themes will remove some of the details that{ggstatsplot}plots typically contains. For example, if relevant,ggbetweenstats()shows details about multiple comparison test as a label on the secondary Y-axis. Some themes (e.g.ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight()) will remove the secondary Y-axis and thus the details as well.- ggplot.component
A
ggplotcomponent to be added to the plot prepared by{ggstatsplot}. This argument is primarily helpful forgrouped_variants of all primary functions. Default isNULL. The argument should be entered as a{ggplot2}function or a list of{ggplot2}functions.- title
The text for the plot title.
- subtitle
The text for the plot subtitle. Will work only if
results.subtitle = FALSE.- caption
The text for the plot caption. This argument is relevant only if
bf.message = FALSE.- ...
Currently ignored.
Details
For details, see: https://indrajeetpatil.github.io/ggstatsplot/articles/web_only/ggcorrmat.html
Summary of graphics
| graphical element | geom used | argument for further modification |
| correlation matrix | ggcorrplot::ggcorrplot() | ggcorrplot.args |
Correlation analyses
The table below provides summary about:
statistical test carried out for inferential statistics
type of effect size estimate and a measure of uncertainty for this estimate
functions used internally to compute these details
Hypothesis testing and Effect size estimation
| Type | Test | CI available? | Function used |
| Parametric | Pearson's correlation coefficient | Yes | correlation::correlation() |
| Non-parametric | Spearman's rank correlation coefficient | Yes | correlation::correlation() |
| Robust | Winsorized Pearson's correlation coefficient | Yes | correlation::correlation() |
| Bayesian | Bayesian Pearson's correlation coefficient | Yes | correlation::correlation() |
Examples
set.seed(123)
library(ggcorrplot)
ggcorrmat(iris)